HTTP vs HTTPS : Understanding Secure Communication
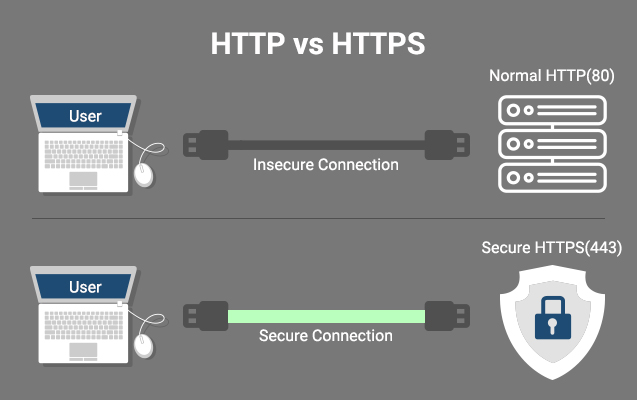
The internet serves as the backbone of modern communication, enabling billions of devices to exchange information. Two protocols HTTP (Hypertext Tansfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) plays a vital role in modern communication through internet. While they might appear similar, their differences significantly impact the security and privacy of data transmission. This article explores these protocols and highlights why HTTPS is essential for secure communication.
What is HTTP?
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a protocol used for transmitting data over the web.
Key Characteristics :
→ Operates on port 80.
→ Data is transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception (e.g., ma-in-the-middle attacks).
→ Suitable for non-sensitive data like accessing public websites.
Limitations :
→ Lack of encryption.
→ Transmitting data can be tampered.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an enhanced version of HTTP with a layer of security added through SSL/TLS encryption.
Key Characteristics :
→ Operates on port 443.
→ Data is transmitted in encrypted form, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity.
→ Commonly used for websites handling sensitive information (e.g., login pages, online banking).
How it works :
→ Uses SSL/TLS protocols to encrypt communication.
→ Employs a digital certificate issed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to verify website authenticity.

Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
| Fetaure | HTTP | HTTPS |
| Encryption | No encryption | End-to-end encryption |
| Port | Port 80 | Port 443 |
| Security | Vulnerable to attacks | Protected against attacks |
| Use Case | Non-sensitive data | Sensitive transactions |
| Perormance | Slightly faster | Slightly slower due to encryption overhead |
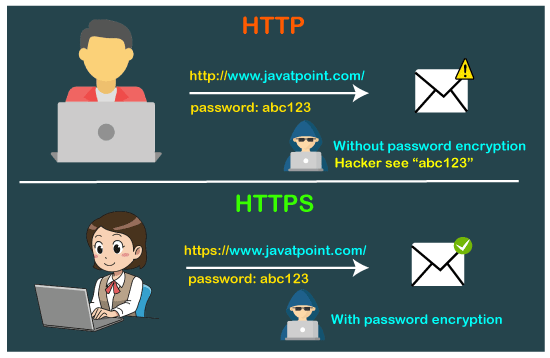
Why HTTPS Matters
Data Security : Prevents unauthorized acces to sensitive data.
User Trust : The padlock icon in browser builds trust with users.
Search Engine Ranking : Google prioritizes HTTPS-enabled websites.
Regularity Compliance : Meets security standards required by GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and other regulations.
Transitioning From HTTP to HTTPS
Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate : Purchase or get a free one (e.g., Let’s Encrypt).
Update Website Links : Replace all HTTP links with HTTPS.
Configure Web Server : Enable HTTPS in your server settings.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS : Set up 301 redirects to maintain SEO rankings.
Conclusion:
Transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS is no longer optional — It is a necessity in today’s digital world. By adopting HTTPS, businesses and individuals ensure privacy, security, and trustworthiness of their online presence. In an era of growing cyber threats, choosing HTTPS over HTTP is a crucial step towards a safer internet.